Compliance Hub
Craft helps you navigate the complex and ever-evolving regulatory landscape so you can stay in compliance. Learn more about important regulations that could impact your business.

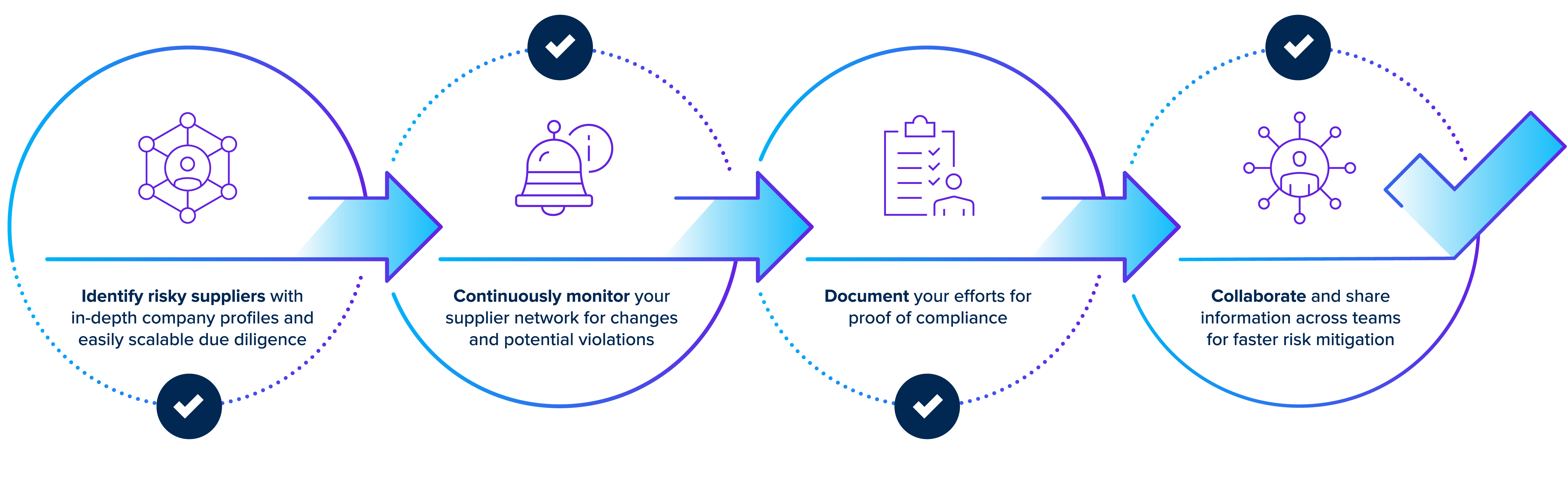
Procurement and supply chain organizations struggle to comply with complex regulations due to inconsistent global standards, limited visibility into suppliers’ actions, and the challenge of maintaining proper documentation for due diligence. Craft identifies high-risk suppliers, streamlines your documentation and audit process, monitors alert signals that reveal potential compliance violations, and helps you optimize your risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
ESG
Financial
Cybersecurity
Forced Labor
Minimize risk and ensure regulatory compliance
Important ESG regulations
Environmental, Social, Governance
The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) mandates that financial market participants disclose how they integrate sustainability risks into their investment decision-making processes and report on the potential adverse impacts of their investments on environmental and social aspects. This regulation aims to enhance transparency, prevent greenwashing, and enable investors to make more informed decisions regarding sustainable investments. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding SFDR is critical as it affects how sustainability risks and impacts are assessed and reported within their organizations. Compliance with SFDR not only ensures regulatory adherence but also strengthens the credibility of an organization’s sustainability claims, making it more attractive to conscientious investors. Additionally, it promotes the integration of sustainability considerations into strategic planning and risk management, supporting long-term resilience and value creation.
For more detailed information, visit the European Commission.
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards are the most widely adopted framework for sustainability reporting, offering guidelines that help organizations communicate their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts effectively. These standards enable organizations to disclose their sustainability performance in a manner that is consistent, comparable, and reliable. For procurement and supply chain professionals, implementing GRI Standards helps ensure transparency and accountability in reporting ESG initiatives and outcomes. This enhances stakeholder trust and supports informed decision-making by providing a clear picture of a company’s sustainability practices. GRI Standards also assist companies in meeting regulatory requirements and improving their sustainability performance by identifying areas for improvement and fostering continuous improvement in ESG practices.
The EU Taxonomy Regulation provides a robust classification system that defines which economic activities can be considered environmentally sustainable. This regulation aims to guide investors towards projects and companies that contribute significantly to environmental objectives, such as climate change mitigation and adaptation, sustainable use of water resources, transition to a circular economy, pollution prevention, and protection of biodiversity. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the EU Taxonomy is crucial as it directly influences investment flows and funding. It requires companies to assess and disclose their activities’ alignment with these sustainability criteria, promoting transparency and accountability in environmental performance. This framework supports sustainable investment decisions and helps organizations demonstrate their commitment to environmental sustainability, thereby enhancing their reputation and compliance with EU environmental regulations.
The EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) aims to improve and standardize sustainability reporting across the EU, ensuring more consistent and comparable corporate disclosures. This directive requires companies to provide detailed information on their sustainability practices, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the CSRD is crucial as it impacts how companies report on and manage their sustainability efforts. Compliance with the CSRD enhances transparency, supports informed decision-making by investors and other stakeholders, and helps companies align with EU sustainability goals. It also encourages companies to integrate ESG considerations into their business strategies and operations, promoting long-term value creation and sustainable development.
The California Transparency in Supply Chains Act (SB 657) requires companies doing business in California to disclose their efforts to eradicate human trafficking and slavery from their supply chains. This regulation aims to provide consumers with information to make informed decisions about the products they buy and to encourage businesses to implement responsible practices in their supply chains. For procurement and supply chain professionals, compliance with this act is crucial to managing reputational risks and ensuring ethical sourcing. By disclosing their efforts to combat human trafficking and slavery, companies can demonstrate their commitment to social responsibility and human rights. This not only enhances their corporate reputation but also helps in building trust with consumers, investors, and other stakeholders.
The EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) requires large companies to disclose non-financial and diversity information, helping stakeholders understand their impact on society. This directive covers various aspects, including environmental protection, social responsibility, employee treatment, respect for human rights, anti-corruption, and board diversity. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the NFRD is essential as it influences how companies report on their sustainability practices and manage non-financial risks. Compliance with the NFRD ensures transparency and accountability, supporting informed decision-making by stakeholders and enhancing the company’s reputation. It also promotes the integration of ESG considerations into business operations and strategy, contributing to sustainable development and long-term value creation.
ISO 14001 sets out the criteria for an environmental management system (EMS) and provides a framework that organizations can follow to improve their environmental performance. This standard helps companies reduce their environmental impact, comply with regulations, and enhance their reputation. For procurement and supply chain professionals, implementing ISO 14001 is essential to managing environmental risks and ensuring sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. Compliance with ISO 14001 demonstrates a company’s commitment to environmental stewardship, which can improve stakeholder relations and competitiveness. Additionally, it supports continuous improvement in environmental performance, helping companies achieve long-term sustainability goals.
The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provides industry-specific standards for companies to disclose financially material sustainability information to investors. These standards focus on ESG issues that are likely to affect the financial condition or operating performance of companies within different industries. For procurement and supply chain professionals, adopting SASB Standards helps in identifying and reporting on sustainability factors that are material to their industry. This enhances the transparency and comparability of sustainability information, supporting better decision-making by investors and other stakeholders. Implementing SASB Standards also helps companies manage ESG risks and opportunities more effectively, aligning their operations with investor expectations and contributing to long-term financial performance.
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provides a set of voluntary, consistent recommendations for companies to disclose climate-related financial risks and opportunities. The aim is to improve transparency and help stakeholders understand the financial implications of climate change on organizations. For procurement and supply chain professionals, the TCFD framework is essential as it guides companies in assessing and managing climate risks and opportunities within their operations and supply chains. By following TCFD recommendations, companies can enhance their risk management practices, improve strategic planning, and attract sustainable investment. Disclosing climate-related financial information also helps organizations demonstrate their commitment to addressing climate change, building trust with stakeholders and aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
The UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights provide a global standard for preventing and addressing human rights abuses linked to business activities. These principles outline the responsibilities of states and businesses to respect, protect, and remedy human rights. For procurement and supply chain professionals, integrating these guidelines into their operations is crucial to mitigating risks associated with human rights violations and ensuring ethical business practices. By adhering to the UN Guiding Principles, companies can demonstrate their commitment to human rights, build trust with stakeholders, and avoid legal and reputational risks. This framework also supports the development of robust human rights policies and due diligence processes, promoting responsible business conduct across the supply chain.
Solution Brief
Understanding ESG Risk
Learn how Craft can help you identify and mitigate ESG risk.
Cybersecurity, data, and privacy regulations
Cybersecurity
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law that regulates how companies collect, store, and manage personal data of EU citizens. It aims to protect privacy and personal data by setting strict guidelines for data processing activities. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding GDPR is vital as it affects how personal data is handled within their operations and supply chains. Compliance with GDPR ensures that companies manage data responsibly, avoid significant fines, and maintain customer trust. It also promotes the adoption of robust data protection practices, supporting overall cybersecurity and risk management efforts.
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is an EU regulation designed to strengthen the digital operational resilience of financial institutions, ensuring that they can withstand, respond to, and recover from all types of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)-related disruptions and threats. This regulation mandates that financial entities implement comprehensive ICT risk management frameworks, conduct regular testing, and ensure robust incident reporting and information sharing.
For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding DORA is essential because it impacts how they select and manage their ICT suppliers and service providers. Compliance requires procurement teams to ensure that their third-party vendors and partners adhere to the stringent cybersecurity and resilience standards outlined by DORA. This includes verifying that suppliers have adequate measures in place to protect against cyber threats and can maintain operational continuity in the face of disruptions.
Non-compliance with DORA can lead to significant financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Therefore, procurement and supply chain professionals must integrate DORA requirements into their vendor selection, contracting, and monitoring processes to mitigate risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) sets cybersecurity standards for defense contractors working with the U.S. Department of Defense. It aims to enhance the protection of sensitive information and ensure that contractors meet specific cybersecurity requirements. For procurement and supply chain professionals, achieving CMMC compliance is crucial to securing defense contracts and maintaining the integrity of sensitive data. The CMMC framework provides a structured approach to improving cybersecurity practices, reducing the risk of cyber threats, and ensuring the protection of national security interests.
For more detailed information, visit the US Department of Defense.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a policy framework of computer security guidance for how private sector organizations in the U.S. can assess and improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber attacks. It is widely recognized as a best practice for managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks. For procurement and supply chain professionals, implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework helps enhance cybersecurity resilience, protect critical information, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The framework supports the development of robust cybersecurity policies and practices, promoting a proactive approach to cyber risk management.
What is NIST 800-53 Revision 5?
NIST 800-53 Revision 5 is a set of guidelines published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) aimed at helping organizations manage and protect their information systems.
Officially titled “Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations,” it provides a comprehensive framework of security and privacy controls to safeguard federal information systems and organizations.
The standard includes a catalog of controls that organizations can use to protect their systems from various threats. The controls are organized into families and are designed to be applicable to a wide range of information systems, including those used by federal agencies and private sector organizations.
Learn More
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California, requiring businesses to disclose how they collect, use, and share personal information. It grants consumers the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal data. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding CCPA is essential to managing data privacy risks and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations. Adhering to CCPA requirements helps build consumer trust, avoid legal penalties, and promote responsible data management practices.
ISO/IEC 27001 specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an information security management system (ISMS). This standard helps organizations protect sensitive information, manage risks, and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. For procurement and supply chain professionals, implementing ISO/IEC 27001 is crucial to safeguarding information assets, complying with regulatory requirements, and building trust with stakeholders. It provides a systematic approach to managing security risks, supporting overall cybersecurity resilience and risk management efforts.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information in the United States. It requires healthcare providers, health plans, and other covered entities to implement safeguards to protect patient data and ensure privacy. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the healthcare industry, understanding HIPAA is essential to managing data protection and compliance risks. Adhering to HIPAA requirements ensures the security of patient information, builds trust with patients, and avoids significant legal and financial penalties.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) provides a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. For procurement and supply chain professionals, complying with PCI DSS is critical to protecting payment card data, preventing data breaches, and maintaining customer trust. It supports the implementation of robust security measures and helps organizations manage cybersecurity risks associated with payment processing.
For more detailed information, visit the Security Standards Council.
The Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) requires federal agencies to develop, document, and implement an information security program to protect their information and information systems. For procurement and supply chain professionals working with federal agencies, understanding FISMA is essential to ensuring compliance with federal cybersecurity requirements and protecting sensitive information. FISMA promotes a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, supporting the development of effective security policies and practices.
For more detailed information, visit Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency.
The Singapore Cybersecurity Act establishes a legal framework for the oversight and maintenance of national cybersecurity in Singapore. It mandates the protection of critical information infrastructure, requires the reporting of cybersecurity incidents, and grants powers to investigate and respond to cyber threats. For procurement and supply chain professionals operating in Singapore, understanding this act is crucial to ensuring compliance with cybersecurity regulations and protecting critical assets. It supports the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures and enhances the overall resilience of information systems.
The NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation imposes stringent cybersecurity requirements on financial services companies operating in New York State. It mandates the implementation of a cybersecurity program, risk assessments, and policies to protect customer data and ensure operational resilience. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the financial sector, complying with this regulation is essential to managing cybersecurity risks, avoiding regulatory penalties, and protecting sensitive information. It promotes the adoption of comprehensive cybersecurity practices, enhancing the security and integrity of financial systems.
For more detailed information, visit New York State Department of Financial Services.
Solution Brief
Understanding Cybersecurity Risk
Learn how Craft can help you identify and mitigate cybersecurity risk.
Important financial regulations
Financial
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) establishes enhanced standards for U.S. public company boards, management, and public accounting firms to protect investors from fraudulent financial reporting. It mandates rigorous internal controls, auditor independence, and corporate governance practices. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding SOX is crucial as it affects financial reporting, internal controls, and compliance requirements. Adhering to SOX ensures transparency, accuracy in financial disclosures, and strengthens overall corporate governance, thereby enhancing investor confidence and mitigating financial risks.
The Dodd-Frank Act introduces comprehensive financial regulatory reforms aimed at reducing risks in the financial system, enhancing transparency, and protecting consumers. It addresses issues such as systemic risk, consumer protection, and financial stability. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the Dodd-Frank Act is essential to navigating compliance requirements, managing financial risks, and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. It also impacts reporting and risk management practices, supporting a more stable and transparent financial environment.
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) provide a global framework for public companies to prepare financial statements, ensuring consistency, transparency, and comparability across international borders. For procurement and supply chain professionals, adopting IFRS is crucial for maintaining accurate financial reporting, facilitating cross-border transactions, and attracting international investment. Compliance with IFRS enhances financial transparency and helps companies meet the expectations of global investors and regulators.
Basel III strengthens regulation, supervision, and risk management within the banking sector to improve its ability to absorb shocks arising from financial and economic stress. It introduces measures such as higher capital requirements, leverage ratios, and liquidity standards. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the banking sector, understanding Basel III is essential to managing financial stability and compliance risks. It supports the development of robust risk management practices, ensuring the resilience and sustainability of financial institutions.
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) prohibits U.S. individuals and entities from bribing foreign government officials to benefit their business interests. It also requires accurate record-keeping and internal controls to prevent corruption. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding FCPA is crucial to managing legal and reputational risks associated with international business transactions. Compliance with FCPA ensures ethical business conduct, supports anti-corruption efforts, and enhances corporate integrity.
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires financial institutions to explain their information-sharing practices to their customers and to safeguard sensitive data. It includes provisions for the protection of personal information and privacy. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the financial sector, understanding GLBA is essential to managing data privacy and security risks. Compliance with GLBA ensures the protection of customer information, supports regulatory adherence, and builds consumer trust.
The European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) aims to increase the stability and transparency of the over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives market throughout the EU. It introduces requirements for the reporting, clearing, and risk management of OTC derivatives. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the financial sector, understanding EMIR is crucial to managing compliance and operational risks. Compliance with EMIR supports market integrity, reduces systemic risk, and enhances transparency in derivative transactions.
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) requires U.S. financial institutions to assist government agencies in detecting and preventing money laundering. It mandates reporting and record-keeping requirements for certain financial transactions. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding BSA is essential to managing compliance and anti-money laundering (AML) risks. Compliance with BSA supports the detection of illicit activities, enhances financial transparency, and protects the integrity of the financial system.
For more detailed information, view the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency.
The Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) aims to improve the functioning of financial markets in the EU and to increase transparency for all market participants. It introduces comprehensive regulations for investment services and trading venues. For procurement and supply chain professionals in the financial sector, understanding MiFID II is crucial to managing compliance and operational risks. Compliance with MiFID II ensures market integrity, enhances investor protection, and supports transparent and efficient financial markets.
The Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD) sets out a framework to combat money laundering and terrorist financing in the EU. It introduces measures such as customer due diligence, reporting obligations, and record-keeping requirements. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding AMLD is essential to managing compliance and financial crime risks. Compliance with AMLD supports the detection and prevention of illicit activities, enhances financial integrity, and protects the reputation of financial institutions.
Solution Brief
Understanding Financial Risk
Learn how Craft can help you identify and mitigate financial risk.
Foreign influence and geopolitical regulations
Foreign Influence
The Export Administration Regulations (EAR) control the export of dual-use goods and technologies, which have both civilian and military applications. These regulations are crucial for maintaining U.S. national security and foreign policy interests by preventing the proliferation of sensitive technologies to adversarial nations or groups. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding EAR is vital to ensuring compliance with export controls, avoiding hefty fines, and mitigating risks associated with unauthorized exports. Compliance with EAR supports the responsible management of international trade activities and helps maintain the integrity of national security.
See more detailed information, visit the International Trade Administration.
The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) reviews and assesses the national security implications of foreign investments in U.S. companies and operations. CFIUS regulations help identify and mitigate potential threats posed by foreign control of critical infrastructure, technology, and sensitive data. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding these regulations is essential to managing risks associated with foreign investments and ensuring compliance with national security standards. Awareness of CFIUS processes supports strategic decision-making and protects vital assets from foreign exploitation.
For more detailed information, visit the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) control the export and import of defense-related articles and services listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML). These regulations ensure that military technologies and services are not accessed by unauthorized foreign entities, thereby protecting national security. For procurement and supply chain professionals, compliance with ITAR is critical to managing legal risks, avoiding severe penalties, and ensuring that sensitive defense technologies are adequately safeguarded. Understanding ITAR supports the secure and lawful management of defense-related exports.
For more detailed information, visit the U.S. Department of State.
The Foreign Agents Registration Act (FARA) requires agents representing the interests of foreign powers in a political or quasi-political capacity to disclose their relationship, activities, and financial receipts. This transparency is intended to inform the U.S. government and the public of foreign influences on domestic policy and opinion. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding FARA is crucial to ensuring compliance when engaging with foreign entities and mitigating risks associated with foreign influence and potential conflicts of interest.
For more detailed information, visit the U.S. Department of Justice.
U.S. Trade Compliance Regulations encompass a variety of laws governing the import and export of goods, services, and technologies. These regulations aim to protect national security, support economic interests, and ensure fair trade practices. For procurement and supply chain professionals, adhering to these regulations is vital to maintaining compliance, avoiding penalties, and ensuring the smooth operation of international trade activities. Understanding trade compliance helps manage risks associated with import/export processes and supports the legal and efficient flow of goods.
For more detailed information, visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
The Foreign Investment Risk Review Modernization Act (FIRRMA) expands the scope of CFIUS to address national security concerns arising from certain foreign non-controlling investments and real estate transactions. FIRRMA aims to protect critical technology, infrastructure, and data from foreign exploitation. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding FIRRMA is essential for managing foreign investment risks and ensuring compliance with national security standards. It supports strategic planning and the protection of sensitive assets in foreign investment scenarios.
For more detailed information, visit the US Congress.
The Unverified List (UVL) identifies parties whose bona fides the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) has been unable to verify. Export transactions involving these parties require additional due diligence and potentially a license. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the implications of dealing with entities on the UVL is crucial for compliance with export controls and avoiding potential legal issues. It ensures that exports are conducted responsibly and in accordance with U.S. national security interests.
For more detailed information, visit the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
The Entity List specifies foreign persons, entities, and governments subject to specific license requirements for the export, reexport, and/or transfer (in-country) of specified items. These entities are involved in activities contrary to U.S. national security or foreign policy interests. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the Entity List is critical for compliance with export regulations and managing risks associated with restricted parties. It helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive technologies and supports responsible export practices.
For more detailed information, visit the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
The Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) imposes sanctions on Iran, North Korea, and Russia, targeting specific foreign transactions and investments that pose a threat to U.S. national security. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding CAATSA is essential to navigating the complexities of international sanctions, avoiding legal penalties, and ensuring compliance with U.S. foreign policy. Compliance with CAATSA helps manage geopolitical risks and supports responsible business practices in global operations.
For more detailed information, visit the U.S. Department of Treasury.
The Global Magnitsky Human Rights Accountability Act allows the U.S. government to sanction foreign government officials implicated in human rights abuses and corruption worldwide. These sanctions include asset freezes and travel bans. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the Global Magnitsky Act is critical to managing risks associated with international human rights violations and ensuring ethical business practices. Compliance with this act supports corporate social responsibility and protects the company’s reputation in global operations.
Solution Brief
Understanding Geopolitical Risk
Safeguard against foreign influence, protect IP, and mitigate disruption from political tensions. Globalization has contributed to an increasingly complex web of multi-tier supplier networks, often obscured by layers of holding companies and limited public information. This lack of transparency enables […]
Forced labor regulations
Forced Labor
The U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act bans imports from China’s Xinjiang region unless companies can prove they are not made with forced labor. This regulation aims to address human rights abuses against the Uyghur population. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act is essential to ensuring compliance, avoiding legal penalties, and promoting ethical sourcing practices. Compliance supports corporate social responsibility and protects the company’s reputation.
The German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act (LkSG) requires large companies to identify, prevent, and mitigate human rights and environmental risks in their supply chains. This regulation aims to improve corporate responsibility and transparency. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the LkSG is crucial to ensuring compliance, managing reputational risks, and promoting ethical sourcing practices. Compliance supports corporate social responsibility and enhances the company’s reputation.
The UK Modern Slavery Act 2015 requires businesses to disclose their efforts to ensure their operations and supply chains are free from modern slavery. This regulation promotes transparency and accountability in addressing human trafficking and forced labor. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the UK Modern Slavery Act is crucial to ensuring compliance, managing reputational risks, and promoting ethical labor practices. Compliance helps build consumer trust and supports corporate social responsibility initiatives.
For more detailed information, visit the UK Government.
The UK Nationality and Borders Act 2022 strengthens measures to identify and support victims of modern slavery and human trafficking. This regulation aims to improve the UK’s response to these issues and protect vulnerable individuals. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the UK Nationality and Borders Act is crucial to ensuring compliance, managing reputational risks, and promoting ethical labor practices. Compliance supports corporate social responsibility and enhances the company’s reputation.
The Australian Modern Slavery Act 2018 mandates large businesses to report on the risks of modern slavery in their operations and supply chains and actions taken to address those risks. This regulation aims to increase transparency and combat human rights abuses. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the Australian Modern Slavery Act is essential to ensuring compliance, mitigating risks, and promoting ethical sourcing practices. Compliance supports corporate social responsibility and enhances the company’s reputation.
The California Transparency in Supply Chains Act (SB 657) requires companies doing business in California to disclose their efforts to eradicate human trafficking and slavery from their supply chains. This regulation aims to provide consumers with information to make informed decisions about the products they buy and to encourage businesses to implement responsible practices in their supply chains. For procurement and supply chain professionals, compliance with this act is crucial to managing reputational risks and ensuring ethical sourcing. By disclosing their efforts to combat human trafficking and slavery, companies can demonstrate their commitment to social responsibility and human rights. This not only enhances their corporate reputation but also helps in building trust with consumers, investors, and other stakeholders.
The EU Forced Labour Regulation aims to ban products made with forced labor from the EU market. This regulation is part of the EU’s efforts to combat human rights abuses in global supply chains. For procurement and supply chain professionals, understanding the EU Forced Labour Regulation is crucial to ensuring compliance, avoiding legal penalties, and promoting ethical sourcing practices. Compliance supports corporate social responsibility and enhances the company’s reputation.
ESG & Diversity
Supplier Intelligence Helps Automotive Firms Comply with the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA)
With the heightened risk of forced labor abuses associated with the auto industry, automotive companies must know their supply chains inside and out. Yet, the sheer size of China’s production capacity combined with opaque global supply chains makes compliance with the UFLPA (and new EV standards) a monumental task.